Tips & Home Remedies for Oral Thrush
What is Oral Thrush?
When a yeast infection occurs within your mouth, it is known as oral thrush. Oral candidiasis, oropharyngeal candidiasis, or simply thrush are all names for the same condition.
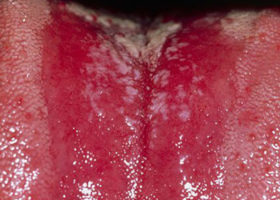
Infants and toddlers are the most common victims of oral thrush. On the inner cheeks and tongue, it produces white or yellowish bumps. Treatment normally gets rid of the bumps.
Oral thrush symptoms
Oral thrush can not cause any symptoms in its early stages. However, as the infection progresses, you can notice one or more of the following symptoms:
White or yellow visible bumps on the inner cheeks, tongue, tonsils, gums, or lips
minor bleeding of surface if the bumps are scraped
soreness or burning in the mouth
a cotton-like feeling in the mouth
the corners of your mouth have dry, cracking skin
A bad taste in your mouth or a loss of taste are both symptoms of trouble swallowing.
Oral thrush can often cause damage to the esophagus, but this is rare. Oral thrush is caused by a fungus that can also cause yeast infections elsewhere in your body.
Causes of Oral Thrush:
An overgrowth of the fungus Candida albicans causes oral thrush and other yeast infections (C. Albicans).
A small amount of Candida albicans will live in your mouth without harming you. Good bacteria in your body help keep C. Albicans under control while your immune system is functioning properly.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are two cancer therapies that can harm or destroy healthy cells. You’ll be more vulnerable to oral thrush and other infections as a result of this.
Oral thrush is more likely to occur in people who have compromised immune systems, such as those who have leukemia or HIV. In HIV patients, oral thrush is a widespread opportunistic infection.
Oral thrush can be exacerbated by diabetes. Diabetes that is uncontrolled weakens the immune system and leads to elevated blood sugar levels. This makes it easier for Candida albicans to thrive.
Oral thrush diagnosis
Your doctor is most likely able to diagnose oral thrush by looking for the characteristic bumps it produces in your mouth. They may take a biopsy of the infected area to confirm the diagnosis in some cases. They can remove a small portion of a bump from your mouth to conduct a biopsy. After that, the sample would be sent to a lab to be checked for C. Albicans.
A throat swab culture or an endoscopy can be used to confirm the diagnosis if your doctor believes you have oral thrush in your esophagus. The doctor takes a tissue sample from the back of your throat using a cotton swab during a throat swab culture. The sample is then sent to a medical laboratory for examination.
Your doctor will use a thin tube with a light and camera attached to perform endoscopy. They test the esophagus by inserting an “endoscope” through your mouth and into it. They can also take a tissue sample for analysis.
Treatment for thrush in the mouth
Your doctor can prescribe one or more of the following medications to treat oral thrush:
Fluconazole (Diflucan), an oral antifungal drug clotrimazole (Mycelex Troche), an antifungal lozenge nystatin (Nystop, Nyata), an antifungal mouthwash that you can swish in your mouth or swab in the mouth of your child
itraconazole (Sporanox), an oral antifungal medication used to treat people with oral thrush who haven’t responded to other therapies and those who have HIV amphotericin B (AmBisome, Fungizone), an oral antifungal medication used to treat serious cases of oral thrush
Oral thrush normally clears up within a few weeks of starting care. However, it is possible that it will return in certain instances.
Adults with recurrent cases of oral thrush for no apparent reason would be evaluated by their healthcare provider for underlying medical conditions that could be leading to the thrush.
In their first year of life, babies can experience several episodes of oral thrush.
Oral thrush home remedies
Your doctor can also suggest home remedies or lifestyle improvements help you treat or prevent oral thrush.
It’s important to maintain good oral hygiene when you’re healing. Here are some pointers:
To stop scratching the bumps caused by thrush, brush your teeth with a gentle toothbrush.
To reduce the chance of reinfection, replace your toothbrush once your oral thrush treatment is over, and clean your dentures properly if you wear them.
Mouthwashes and mouth sprays can only be used if the doctor has recommended them.
Adults can benefit from some home remedies to alleviate thrush symptoms.
For e.g., rinsing your mouth with one of the following may be beneficial: saltwater.
a baking soda and water solution
a mixture of lemon juice and water
a solution of apple cider vinegar and water
It may also be helpful to consume probiotic yogurt or take a probiotic supplement. Before offering an infant some nutrients, consult a doctor.
Is thrush of the mouth contagious?
It’s possible to transfer the fungus that triggers oral thrush onto someone else if you kiss them if you have it. Oral thrush could grow in that individual in some cases. Oral thrush is caused by a fungus that often induces yeast infections in other areas of the body. It’s possible for you to spread the fungus from one section of your body to another. You can transmit the fungus to your partner by vaginal sex, anal sex, or oral sex if you have oral thrush, a vaginal yeast infection, or a penile yeast infection.
If you have a vaginal yeast infection while pregnant, the fungus will be passed to your baby during birth. You can transmit a yeast infection to your baby if you have a breast yeast infection or a nipple yeast infection while breastfeeding. If your baby has oral thrush and breastfeeds, they will pass the fungus on to you.
C.Albicans may not often cause oral thrush or other forms of yeast infection when it is spread from one individual to another.Since Candida albicans is so common in our setting, getting a yeast infection doesn’t necessarily mean you got it from anyone else.

Hailey - 9 months ago