
There exists important landmarks i.e. anatomical landmarks in the upper arch of the oral cavity which are of importance while fabricating a denture to the patient. The ultimate support for maxillary denture comes from the hard palate and the soft tissues that increases the surface area of the basal seat.
These anatomical structures are important because the denture and these tissues comes in contact for long duration of time; also to decide upon the distribution of forces in various locations of the foundation area.
Anatomical Structures can be Classified into Three Types:
- Limiting Structure
- Supporting Structure
- Relief Areas
Limiting Structure Includes:
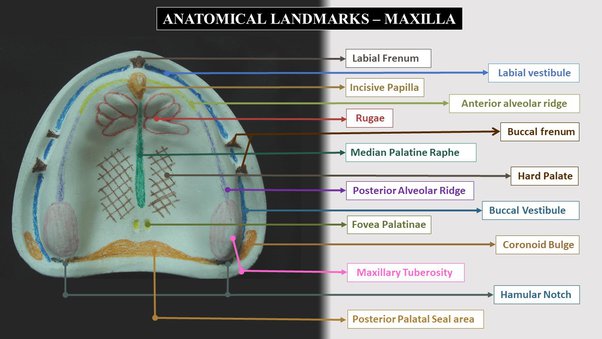
- Labial Frenum
- Labial Vestibule
- Buccal Frenum
- Buccal Vestibule
- Hamular Notch
- Posterior Palatal Seal Area
Supporting structures:
Support is the resistance to the displacement towards the basal tissue or underlying structures.
Primary stress bearing area / Supporting area:
- The horizontal portion of the hard palate lateral to the midline
- Posterolateral slopes and slopes of residual alveolar ridge
Secondary stress bearing area / Supporting area:
- Rugae area - set at an angle to residual ridge
- Maxillary Tuberosity
Relief Areas Includes:
- Incisive papilla - pad of fibrous connective tissue over the incisive foramen
- Mid-palatine raphe - Extends from incisive papilla to distal end of hard palate
- Crest of the residual alveolar ridge
- Cuspid eminence
- Fovea palatine - Bilateral indentations near the midline of palate
- Labial frenum - Fold of mucous membrane at the median line
- Buccal Frenum - Single or double folds of mucous membrane. It is broad and fan shaped
- Labial vestibule - Labial to buccal frenum. Muco-gingival line limits upper border. Record adequate depth/width. Overextension causes instability/soreness
- Buccal Vestibule - Located buccal frenum to hamular notch. It records adequate depth/width. Improper extension causes instability/soreness
- Hamular notch - Is a soft area of areolar tissue between distal surface of tuberosity and the hamular process of the medial pterygoid plate. Aids in achieving posterior palatal seal.Overextension causes soreness whereas underextension causes poor retention.
- Posterior Palatal Seal Area - The soft tissue area at or beyond the junction of the hard and soft palates on which pressure within physiological limits, can be applied by a complete denture to aid in its retention
- Vibrating Line - Is an imaginary line across the posterior part of the palate marking the division between the movable and immovable tissues of the soft palate
- Residual alveolar ridge - The portion of the residual bone , soft tissue covering that remains after the removal of teeth.It is subjected to resorption
These are a few important anatomical landmarks of maxilla / upper arch to be considered when fabricating a denture to the patient. Proper knowledge of these anatomical landmarks helps to achieve desired clinical outcomes of the treatment.
Article by:
Dr. Siri P. B.





Hailey - 9 months ago