 Dentist Channel Online
Dentist Channel Online
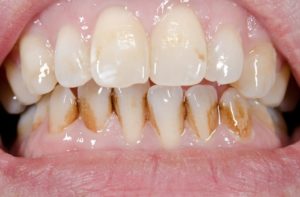
Tooth colour varies from pearl white to pale yellow. Any deviations from these colours is termed as dental stains or dental discolorations. Let us look into a few of the reasons for this clinical situation and ways to tackle it.
Stains limited to the external surface of the tooth i.e. due to external factors
Stains incorporated within the tooth structure can be external factors or internal factors
Stains present due to formation of calculus and soft deposits.
It can be due to poor oral hygiene, plaque depositing on the tooth, any food pigments, smoking, chlorhexidine, tobacco, metallic salt, chromogenic bacteria etc.
It can be due to a few of the drugs, developmental alterations of the tooth during tooth development stages, non-vital tooth, internal resorption of the tooth, a condition called as fluorosis, early jaundice, blood borne pigments, erythroblastosis foetalis etc
Management of Dental Stains
The management of extrinsic stains is easier than intrinsic. Close observation of discoloration of the teeth is the first step to be taken. Once in six months visit to the dentist and getting scaling / cleaning of the teeth done avoids the severity of extrinsic tooth discoloration. Oral hygiene practice helps in avoiding this situation as well.
Intrinsic stains on the other hand requires a different approach. If its due to developmental disturbances of the teeth, the tooth is usually less mineralized. It shows pitting on the surface of the teeth. Here, along with removal of stains, it also includes esthetic and functional replacement of missing tooth structure.
A few of the drugs like tetracycline if taken by the pregnant woman in the third trimester of pregnancy, leads to discoloration of future teeth of the child. Dental stains can also occur when the drug is administered to the child in infancy and early childhood. It can be generalized or limited to specific parts of the tooth, depending up on at what period of development the drug was administered. It also depends on the dosage duration and the type of the drug. The colour of the tooth may vary from light green to dark yellow or a grey brown.
Non-vital tooth discolouration is managed by non-vital bleaching approach. Bleaching is one of the techniques in treating discoloration of both vital and non-vital teeth.
Restorative materials such as silver amalgam can cause grey to black dental stains, copper amalgam causes bluish green dental stains. Mineral trioxide aggregate. A dental material causes grey stain, composites, a tooth coloured restorative material causes light brown stain on the teeth.
Internal resorption causes pink discolouration of the teeth, incipient caries causes white chalky spots and cervical caries displays black discolouration. Recurrent caries shows up grey to brown and rampant caries appears black to dark brown.
Thus, dental stains are commonly encountered situation in dental practice. The advancements in dental materials and technology has made it easier to treat dental stains with good results.
Author: Dr. Siri P. B.



Hailey - 9 months ago