 Dentist Channel Online
Dentist Channel Online
The main features to be looked out are for
Normal Anatomy
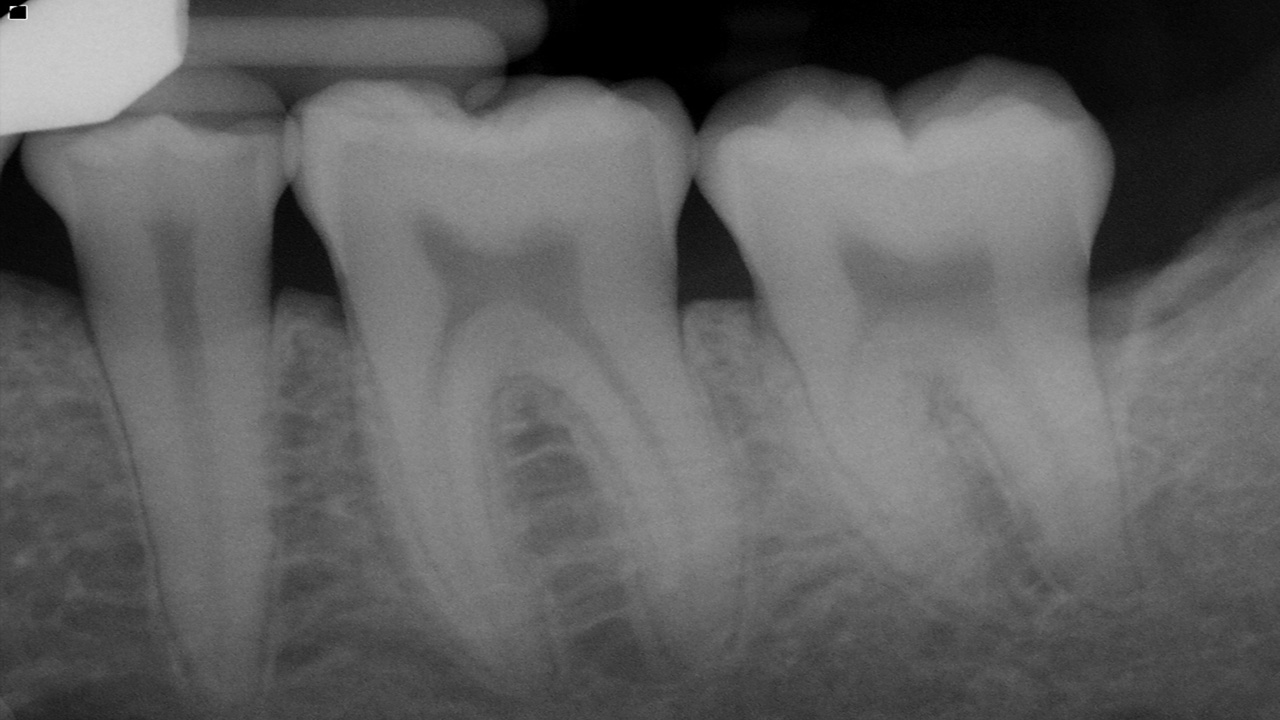
A thin layer of opaque cortical bone often covers the alveolar crest. The height of the crest lies at a level approximately 0.5 to 2.0 mm below the level of the CEJs of adjacent teeth. Between posterior teeth the alveolar crest also is parallel to a line connecting adjacent CEJs. Between anterior teeth the alveolar crest usually is pointed and may have a well-defined cortex.
Between the anterior teeth, the normal alveolar crest is pointed and well corticated, coming to within 0.5 to 2.0 mm of the adjacent CEJs. The normal alveolar crest lies 0.5 to 2.0 mm below the adjacent CEJ and forms a sharp angle with the lamina dura of the adjacent tooth.
The periodontal ligament (PDL) space is often slightly wider around the cervical portion of the tooth root, especially in adolescents with erupting teeth. In this situation, if the lamina dura still forms a sharp, well-defined angle with the alveolar crest, the condition is a variant of normal and is not an indication of disease. The thickness of alveolar crests varies and may be very thin coronally. This may appear radiographically as an increase in radiolucency toward the crest.
The PDL varies in width from patient to patient, from tooth to tooth in the individual, and even from location to location around one tooth. Usually it is thinner in the middle of the root and slightly wider near the alveolar crest and root apex, suggesting that the fulcrum of physiologic movement is in the region where the PDL is thinnest. The shape of the tooth creates the appearance of a double PDL space. When the x-ray beam is directed so that two convexities of a root surface appear on a film, the double PDL space is seen.
General Radiographic Features of Periodontal Disease
Article by Dr. Siri P. B.

Hailey - 9 months ago