 Dentist Channel Online
Dentist Channel Online
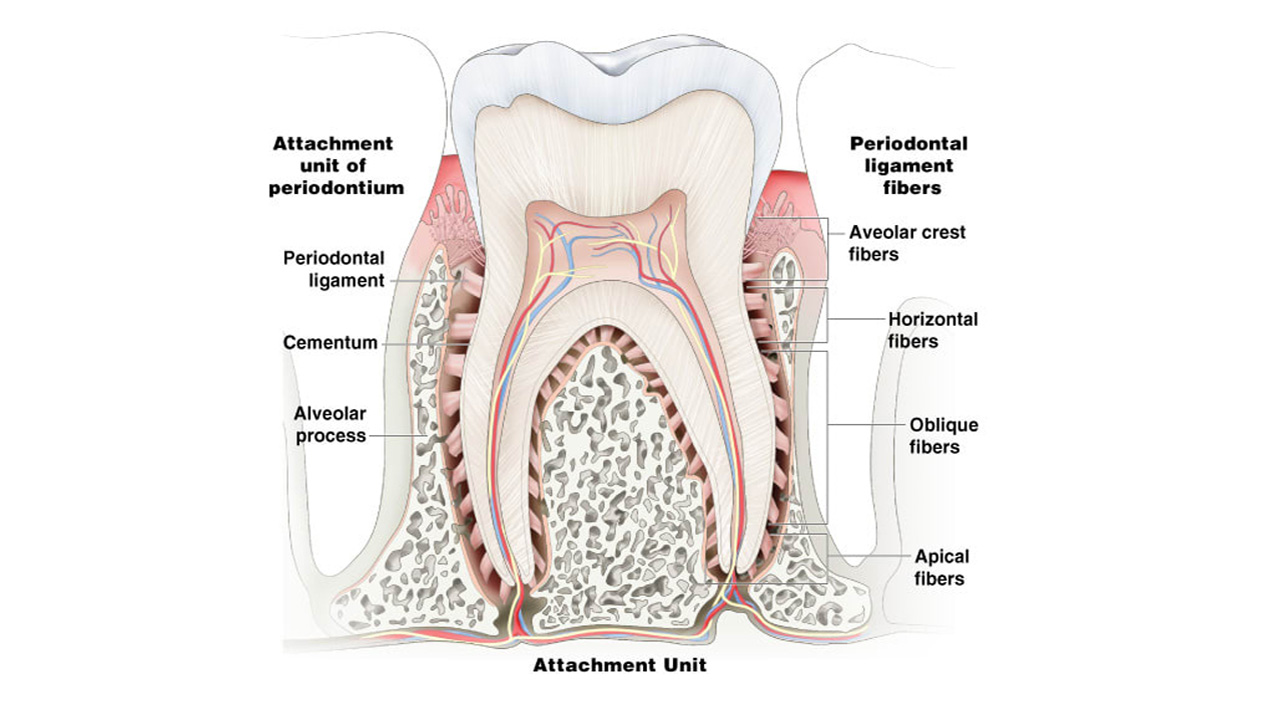
Tooth-supporting structures include, the periodontal ligament, cementum and alveolar bone. The periodontal ligament is a connective tissue structure that surrounds the root and connects it with the bone. The periodontal ligament space has the shape of an hourglass and is narrowest at the mid-root level.
Periodontium has been divided into two parts: the gingiva, the main function of which is protecting the underlying tissues, and the attachment apparatus, composed of the periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone. Periodontal ligament in short is called as PDL. It is composed of a complex vascular and highly cellular connective tissue that surrounds the tooth root and connects it to the inner wall of the alveolar bone. Width of PDL is about 0.2 mm.
Cells of periodontal ligament are categorized as -
Extracellular Components includes –
Periodontal fibers: They are the most important elements of the periodontal ligament. It includes Trans-septal group, alveolar crest, horizontal, oblique, apical and interradicular fibres. They are collagenous and arranged in bundles. Small collagen fibers run in all directions along with the principal fibres, forming a plexus called the indifferent fiber plexus.
The space between cells, fibers, blood vessels and nerves in the periodontal space is occupied by ground substance which is made up of glycosaminoglycans such as hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans and glycoproteins such as fibronectin and laminin. It contains around 70 percent water content.
Structures present in the connective tissue are the blood vessels, lymphatics, nerve innervation and cementicles.
Functions of Periodontal Ligament includes –
The primary role of periodontal ligament is to support the tooth in the bony socket. Periodontal ligament is shaped like an hourglass and since it is narrowest in the middle region of the root it seems to be the fulcrum of physiologic movement.
Article by Dr. Siri P. B.

Hailey - 10 months ago